1. Is command
The ls command is commonly used to identify the files and directories in the working directory. This command is one of the many often-used Linux commands that you should know.
This command can be used by itself without any arguments and it will provide us the output with all the details about the files and the directories in the current working directory. There is a lot of flexibility offered by this command in terms of displaying data in the output. Check the below image for the output.

2. pwd command
The pwd command is mostly used to print the current working directory on your terminal. It is also one of the most commonly used commands.
Now, your terminal prompt should usually include the entire directory. If it doesn’t, this is a quick command to see which directory you’re in. Another purpose for this command is when creating scripts because it can help us find the directory in which the script was saved. The below pictures are the output with the command.
Command:

Output:
3. mkdir command
This mkdir command allows you to create fresh directories in the terminal itself. The default syntax is mkdir <directory name> and the new directory will be created.
For example, if you want to create a directory as “GeeksforGeeks” then the basic syntax would be:
mkdir GeeksforGeeks
In case you want to create another directory inside the main directory GeeksforGeeks to store projects, you can use the following command to do so. mkdir GeeksforGeeks/projects
Command:
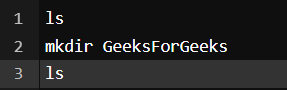
Output:
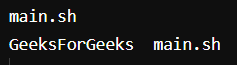
You can see we used ls first to see the directories present there and then mkdir to create another directory followed by ls to view the created directories.
4. cd command
The cd command is used to navigate between directories. It requires either the full path or the directory name, depending on your current working directory. If you run this command without any options, it will take you to your home folder. Keep in mind that it can only be executed by users with sudo privileges.
Command:
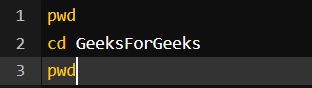
Output:
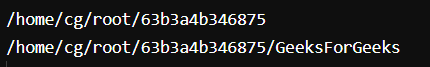
Here we used pwd to view the current directory for reference and then we used cd GeeksforGeeks to switch the directory and with again pwd command we can see the output is the switched directory, i.e – GeeksforGeeks
5. rmdir command
The rmdir command is used to delete permanently an empty directory. To perform this command the user running this command must have sudo privileges in the parent directory.
Command:
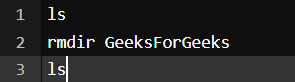
Command to remove the directory
Output:
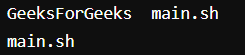
Here we used the ls command to check the directories present there and used rmdir <directory name> to delete the directory and again the ls command to view the directories after deleting the same.
6. cp command
The cp command of Linux is equivalent to copy-paste and cut-paste in Windows.
Command:
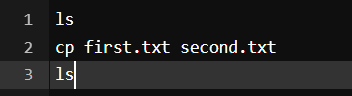
Output:
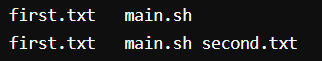
Here we used ls to view the files and then used cp to copy the files of first.txt to second.txt and again used ls command to view the updated files.
7. mv command
The mv command is generally used for renaming the files in Linux.
Command:
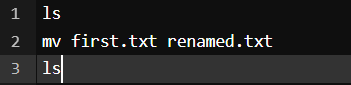
Output:
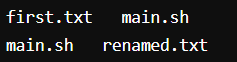
Here we used the ls command to check the directories and then used mv <file name> <Renamed file name> to rename the files, and then again we used the ls command to view the renamed file as you can see in the output screenshot.
8. rm command
rm command in Linux is generally used to delete the files created in the directory.
Command:
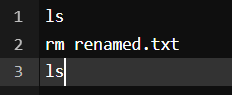
Output:
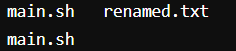
You can see as we wrote the ls command to view the files in the terminal and then rm <file name> to delete the files and again we had the ls command to check the update.
9. uname command
The uname command is used to check the complete OS information of the system. Check out the command and the output below
Command:
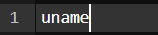
Output:
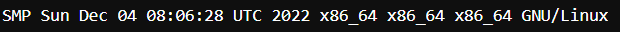
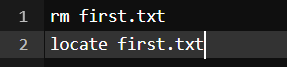
10. locate command
The locate command is generally used to locate the files in the database. Use an asterisk (*) to search for content that contains two or more words. As an example: locate first*file. This command will search the database for the files that contain these two names first and file.
Command:
Output:
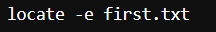
We first used the rm command to delete the file and then used locate command to find the file in the database which in return has given the output with a -e as the file was removed.
11. touch command
The touch command creates an empty file when put in the terminal in this format as touch <file name>
Command:
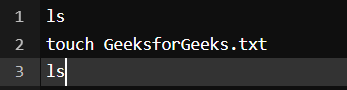
Output:
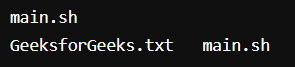
We used the ls command to check the current directories in the terminal and then used the touch command to create an empty file and then again we used ls to find out the created file in the terminal.
12. ln command
The ln command is used to create a shortcut link to another file. This is among the most important Linux commands to know if you want to operate as a Linux administrator.
Command:
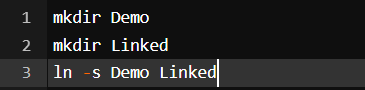
Output:

Here we used mkdir to create two directories and then we used ln with an -s to create a soft link in it.
13. cat command
The cat command is the simplest command to use when you want to see the contents of a particular file. The only issue is that it simply unloads the entire file to your terminal. If you want to navigate around a huge file, should use less command alternatively.
Command:
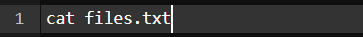
Output:
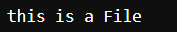
14. clear command
The clear command is a standard command to clear the terminal screen.
Command: *This was the terminal before the command.
Output:
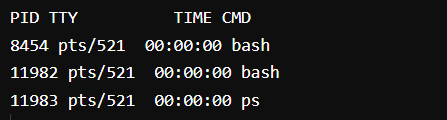
15. ps command
ps command in Linux is used to check the active processes in the terminal.
Command:

Output:
16. man command
The man command displays a user manual for any commands or utilities available in the Terminal, including their name, description, and options.
Command to view the full manual:
man <command name>
For example, suppose you want to look up the manual for the ls command: man ls
Command:
Output:

17. grep command
The grep command is used to find a specific string in a series of outputs. For example, if you want to find a string in a file, you can use the syntax: <Any command with output> | grep “<string to find> “
For Example:
cat Files.txt | grep “new”
Command:
Output:
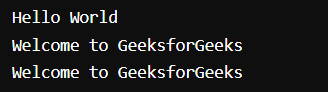
In this command, we first used cat <file name> to view the content of the file, and then we used cat <file name> | grep “string” to check the string in it.
18. echo command
echo command in Linux is specially used to print something in the terminal
Command:

Output:

19. wget command
The wget command in the Linux command line allows you to download files from the internet. It runs in the background and does not interfere with other processes.
Here is the basic syntax: wget [option] [url]
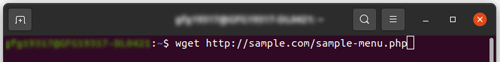
Command:
wget http://sample.com/sample-menu.php
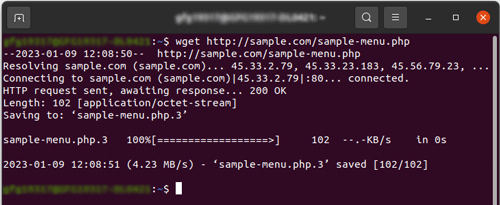
Output:
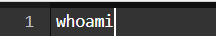
20. whoami command
The whoami command provides basic information that is extremely useful when working on multiple systems. In general, if you are working with a single computer, you will not require it as frequently as a network administrator.
Command:
Output:

21. sort command
The sort command is used generally to sort the output of the file. Let’s use the command and see the output.
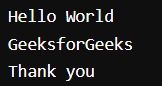
Command: (We are using the cat command to see the file content)
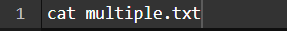
Output: (The content of multiple.txt file in the terminal)
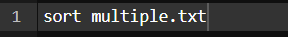
Now we will sort the outcome using the sort command
Command:
Output:
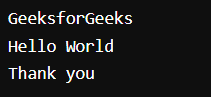
Here first we checked the file content using the cat command and then we sorted it alphabetically using the sort command.
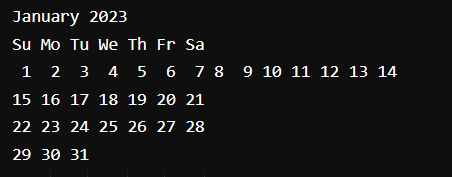
22. cal command
The cal command is not the most famous command in the terminal but it functions to view the calendar for a particular month in the terminal. Let’s see how this works.
Command:
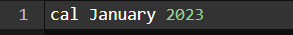
Output:
23. whereis command
whereis command in Linux is generally used to see the exact location of any command typed after this. Let’s see how this performs.
Command:
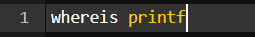
Output:

24. df command
df command in Linux gets the details of the file system.
Command:
Output:
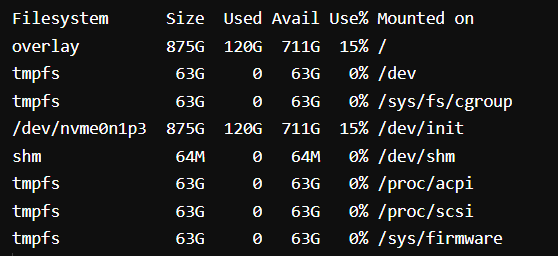
Here we have used df -h as simply typing df will return the output in bytes which is not readable, so we add -h to make the outputs more readable and understandable.
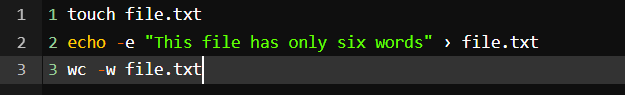
25. wc command
wc command in Linux indicates the number of words, characters, lines, etc using a set of options.
wc -w shows the number of words
wc -l shows the number of lines
wc -m shows the number of characters present in a file
Let’s see one example of these options
Command:
Output:
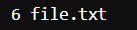
Here we used the touch command to create a text file and then used the echo command to input a sentence that contains six words and we used the wc -w command to calculate the number of words in it.
